
Daily activities are always limited when the lower back is in pain. It is a common condition that affects many people of all ages. There are many causes of back pain, so getting the right diagnosis is important in finding the right treatment method. Individuals can use traditional pain management techniques like medications, physical therapy, and massage. Newer technologies allow people to incorporate electrotherapy into their routines. However, epidurals and surgery may be necessary in severe cases.
Back pain can happen suddenly as a result of injury or develop gradually due to an underlying health issue. If left untreated, the condition may worsen. Thus, dealing with back pain requires careful attention and proper management. It is vital for individuals to seek medical attention and explore various techniques to find the most effective method. This guide will explore the causes of backaches and the treatment methods available.
Jump to a Section:
What Does It Mean When Your Lower Back is in Pain?
When the lower back is in pain, it could indicate a number of different conditions or issues. It could be specific and non-specific. Specific back pain is when there is an identified cause, such as a disease or a structural problem. It could also be a referred pain, which is symptoms coming from another part of the body.
On the other hand, non-specific back pain does not have a particular cause. It could be short-term or persisting. Thus, the pain may go away on its own or need long-term pain management. Moreover, sore muscles, nerve compression, and spinal problems typically contribute to back pain. Targeting these areas can help alleviate the symptoms.
Additionally, persistent back pain is a way the body communicates that something is wrong and needs attention. Therefore, symptoms or discomfort that endures for at least a week may require a doctor consultation. It is also vital to monitor how the body reacts to treatment methods and make adjustments as necessary.
Impacts on Daily Life
- Backaches can make it difficult to perform simple back functions such as bending, lifting, or reaching.
- It causes discomfort in sitting for prolonged periods, thereby affecting work productivity and concentration.
- Back pain can result in poor sleep quality, leading to fatigue and decreased energy levels throughout the day.
- It can limit physical activities and exercise, hindering overall fitness and strength.
- Back pain may affect mobility, making it harder to walk, climb stairs, or perform activities that require movement.
- Chronic pain can impact mental health, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression.
- It can disrupt social interactions due to limitations in participating in recreational activities.
Types of Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain can be categorised into acute, sub-acute, and chronic pain. Acute pain happens suddenly and lasts for a few days to weeks. It may only require rest or minimal interventions to handle the symptoms. Sub-acute pain may occur suddenly or develop over time. It can last for 4 to 12 weeks.
Chronic back pain persists for at least 12 weeks and occurs frequently. It is often due to an underlying cause. Furthermore, the pain can be localised or widespread. Localised pain is confined to a particular area of the body. Meanwhile, widespread pain spreads to the entire back and may extend to other parts of the body.
An understanding of the lower back anatomy is vital to determining the back pain causes and appropriate treatments. Muscular pain occurs due to swollen or sore muscles. Degeneration or abnormalities in the lumbar spine can result in radicular pain. This often involves discs and compressed nerves. Thus, knowing these factors can help manage the condition effectively.
Acute Pain vs Chronic Pain
Acute pain refers to sudden and short-term pain. The cause is often known or specific, such as muscle spasms, trauma, or strain on the muscles and ligaments. In addition, the symptoms can be intense but usually resolves with rest and self-care measures. It will also subside after healing of the damaged area.
Chronic pain refers to persistent or long-lasting pain that lasts for more than 12 weeks. The cause may be due to an underlying condition, while others may occur for no apparent reason. Due to its long-term nature, chronic pain can significantly impact the quality of life and may require ongoing care.

Causes of Lower Back Pain
A variety of factors can cause acute or chronic lower back pain. Firstly, there are mechanical or structural problems. These are conditions that affect the lumbar spine, intervertebral discs, muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the back. Muscle or ligament strain occurs due to overexertion or incorrect body mechanics during heavy lifting. Degenerative disc diseases are also common causes, like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
Secondly, inflammatory conditions such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to lower backaches. They manifest in swelling, heat, and redness in the spinal joints and other areas. In particular, ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis of the spine. Other conditions include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and sciatica or nerve irritation.
Other back pain causes include osteoporosis, endometriosis, kidney stones, and infections. In rare cases, tumours develop on the spine and can cause pain that worsens over time. Lastly, lifestyle factors like obesity, lack of exercise, and poor posture are common risk factors for chronic back pain development.
Symptoms to Look For
The symptoms of lower backaches vary depending on the cause of the pain. The most common symptoms include a dull ache that can be accompanied by stiffness or limited mobility. This pain may be constant or intermittent, and it can range from mild to severe.
Shooting or sharp pains are common in sciatica or nerve compression. It often radiates to other areas, such as down the legs. Some pain may manifest during movement, such as when standing or bending the back. In other cases, the symptoms may worsen when resting or prolonged periods of inactivity and may get better with light movements.

Lower Back Pain Diagnosis
It is vital to consult a doctor when the lower back is in pain constantly. A physician can run a series of tests to diagnose the cause of the back pain. It involves a systematic approach, including assessment of medical history and physical examination. The doctor may ask the patient about specific symptoms, when the pain started, and if there were any triggering events.
Physical examination involves tests of the range of motion, strength, and reflexes to identify any underlying issues. After the initial assessment, further diagnostic tests can help get a more accurate diagnosis. It may include imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. These can help visualise the structures of the spinal column to identify any abnormalities.
In some cases, additional specialised tests may be required to pinpoint the specific cause of back pain. It includes nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), or diagnostic injections. These approaches can help determine if the pain is related to nerve damage or inflammation. Overall, a comprehensive and thorough approach is essential to accurately identify the cause and develop an effective treatment plan.
Risks When Untreated
- There is a risk of developing complications, such as nerve damage, spinal instability and mobility limitations.
- The underlying cause may worsen. This is likely in progressive conditions like arthritis, degenerative disc disease, and infection.
- The range of motion may continue to decrease gradually.
- Ignoring back pain can lead to further injury or damage to the spine.
- Chronic pain may affect mental health, contributing to stress, anxiety, or depression.
- Chronic pain can limit physical activity. Fewer activities can make the person more prone to diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and weaker muscles.
- Untreated back pain can lead to permanent disabilities.

Lower Back Pain Treatment: Medications
The most common treatment method when the lower back is in pain is medication. It is affordable, accessible, and can provide fast relief. There are various types of medications that can help in relieving pain and discomfort. The first type is Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). They are first-line treatment when it comes to relieving pain due to inflammation.
In addition, paracetamols or acetaminophen can be effective in treating acute back pain. Taking paracetamols at regular intervals is suitable for treating acute back pain. Moreover, muscle relaxants help alleviate pain through their sedative effects. They work on the skeletal muscles and improve muscle tone. As a result, it helps reduce muscle spasms and promote relaxation.
For severe pain, a health professional may prescribe opioids. These medications are stronger painkillers and can be effective for acute pain management. Likewise, regulated or supervised use is important for chronic pain. NSAIDs and paracetamols are over-the-counter drugs and are suitable for mild to moderate pain, while muscle relaxants and opioids require prescription.
Pros & Cons of Medication
Pain medications can provide immediate relief for various pain conditions. NSAIDs and paracetamol are generally safe for short-term use. It works by inhibiting specific enzymes that contribute to pain or inflammation. Additionally, they are cost-effective treatments. Oral pain relievers are easily accessible in pharmacies.
However, there are several drawbacks and risks. Long-term use can come with potential side effects such as stomach ulcers, kidney problems and liver damage. Muscle relaxants may cause drowsiness and impair cognitive functions, affecting activities that require concentration. Furthermore, opioids carry a high risk of addiction. Misuse can also lead to respiratory depression.

Lower Back Pain Treatment: Injections
Injections can be an effective treatment for lower back pain when oral pain relievers may not work. This technique delivers medication directly to the affected area, providing targeted relief. There are several types of injections that can be used. A common type is epidural steroid injection. It involves delivering corticosteroids, a powerful anti-inflammatory medication. Administration involves injecting into the epidural space.
Another option is selective nerve block injection. It involves injecting a local anaesthetic directly into or around the affected nerve root. It works by blocking them from sending pain signals, providing temporary relief. This can also help identify where the pain is originating from. It is commonly used to ease pain after surgery or manage back pain during labour.
Moreover, there is facet joint injection. It is a minimally invasive procedure that targets the small joints in the spine called facet joints. It contains a local anaesthetic and steroids that provides pain relief and reduces inflammation in the area. Administration involves injecting into the facet joints in the tailbone region.
Pros & Cons of Injections
Injections deliver medication directly to the affected area, providing targeted relief. They can be more effective than oral painkillers in some cases, especially for inflammatory-type pain or nerve irritation. It also has a longer-lasting effect than oral medicines. In addition, they can provide relief without the need for surgery.
While they are generally safe, there are some drawbacks to be aware of. The procedure itself can be uncomfortable for some individuals. There is also a small risk of infection. In rare instances, it can lead to low blood pressure, severe headaches, and nerve damage. The effects may also vary from person to person.
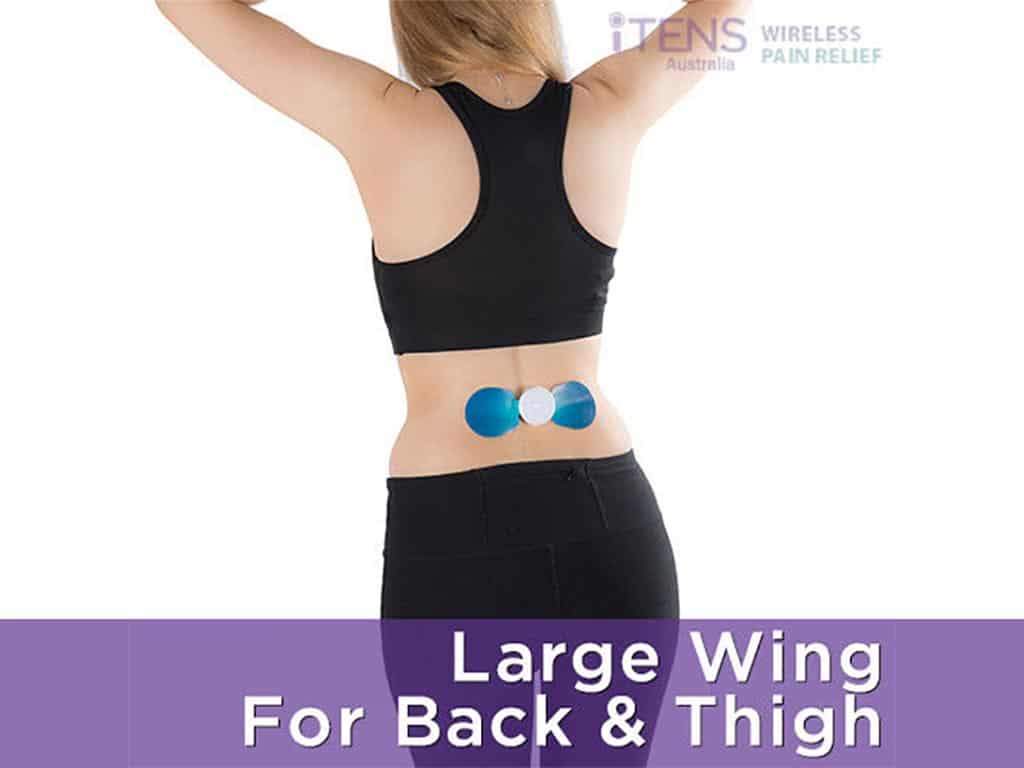
Lower Back Pain Treatment: TENS
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive treatment option when the lower back is in pain. It involves using a small, battery-operated device that delivers low-voltage electrical currents to the body. The TENS machine has adjustable settings to customise the intensity and frequency of the electrical pulses. Therefore, it can cater to different types of pain and pain levels.
The theory behind TENS therapy is that the electrical currents stimulate the sensory nerves and block the transmission of pain signals. It induces certain nerve fibres in the spinal cord that act as a gating mechanism to close, preventing the pain signals from reaching the brain. Another method is to promote the production of endorphins, the natural painkillers of the body.
To facilitate the treatment, individuals attach the adhesive electrode pads on the pain site, typically at the lower back on either side of the spinal cord. Then, turn on the TENS machine and adjust the settings, starting at the lowest intensity. Users should gradually increase the intensity until the sensations feel strong but painless and comfortable.
Pros & Cons of TENS
Pros
- TENS does not have adverse or long-term side effects.
- It offers versatile and comprehensive pain management that includes different types of pain conditions.
- The TENS machine has adjustable settings, allowing customisation of the treatment according to individual conditions and comfort levels.
- The portable device is convenient and easy to use anywhere.
Cons
- TENS therapy may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy and heart problems.
- Individual responses to the treatment can vary.
- It may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
- It is not advisable to use while in water or while sleeping or driving.

Lower Back Pain Treatment: Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a widely recommended treatment option for lower back pain. It involves the use of exercises, stretches, and manual techniques to improve the lower back condition. One of the primary goals of physical therapy is to reduce pain while promoting healing and recovery. Physical therapists work closely with the patient to create personalised treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals.
Additionally, physical therapy focuses on improving posture and body mechanics. Poor posture, whether from sitting or standing, can contribute to back pain. Physiotherapists can teach proper body mechanics, such as lifting heavy weights with the legs instead of the back. By correcting these habits, individuals can reduce the strain on the lower back and alleviate pain.
Individuals can also focus on improving muscle strength and flexibility. There are guided exercises that help strengthen lower back and abdominal muscles to increase their stability and mobility. This aims to improve the skeletal muscles and prevent the risk of injuries. A combination of these techniques can help manage and alleviate backaches effectively.
Pros & Cons of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy offers a personalised treatment for back pain. This ensures that it addresses the root cause of the pain and focuses on improving overall functionality. Moreover, it is a natural approach using exercises to target specific areas of the body. This minimises the need for surgery or other invasive procedures.
However, physical therapy can be time-consuming. Thus, it requires commitment and consistency to see significant results. Individuals may need to attend multiple sessions over a period of weeks or months, which can incur high costs. In addition, it may not be suitable for some individuals with severe medical conditions.

Lower Back Pain Treatment: Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is another effective treatment option for individuals experiencing lower back pain. It involves the manipulation of soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and ligaments, to promote relaxation and alleviate pain. Consequently, it helps to reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and increase the range of motion. Massage therapists use various techniques, including kneading, stretching, and applying pressure.
Massage affects the muscular and skeletal systems up to deeper layers to promote healing. The increase in blood flow delivers nutrients and oxygen to the muscles and tissues, accelerating their recovery. Furthermore, it helps flush out waste products and toxins from the body, reducing inflammation and promoting overall wellness.
Many individuals experience significant pain reduction in their lower back after a series of therapeutic massages. Stretching and manipulation techniques also improve the flexibility and mobility of the muscles. Regular massage therapy sessions can help maintain this flexibility and reduce the frequency of back pain episodes. Overall, it is a holistic approach that can address the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Pros & Cons of Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is a simple yet effective method of pain management. It targets pressure points to alleviate pain without the use of medications. Aside from pain relief, it helps lower high blood pressure, increase energy levels, and reduce stress. Moreover, it is safe for most people and has minimal side effects.
Unfortunately, massage may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with deep vein thrombosis or skin infections may need to avoid this treatment method. It can cause temporary side effects, such as bruising and soreness. Another disadvantage is the cost of regular sessions. Specific massage techniques are necessary for effective results.

Lower Back Pain Treatment: Surgery
Surgery is often the final treatment option when the lower back is in pain. It involves invasive procedures to correct underlying issues and structural abnormalities and alleviate pressure on the nerves. A health professional may recommend surgery when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. This method can provide long-lasting relief for individuals with severe or chronic pain.
There are different surgical options available depending on the underlying cause of pain. For instance, herniated disc surgery or discectomy involves removing the portion of the disc that is pressing on the nerve. On the other hand, spinal fusion surgery aims to stabilise the affected vertebrae by joining two bones together.
A healthcare professional will examine the condition of the patient to determine if they are a candidate for surgery. Factors such as the severity of the pain, the presence of nerve compression, and the overall health of the individual are taken into account. However, surgery for back pain does not guarantee complete resolution of symptoms. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes when considering surgery.
Pros & Cons of Surgery
Pros
- It can give a permanent solution for chronic back pain by correcting structural issues.
- Surgery can provide relief for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- It is a viable treatment option when medications and physical therapy are not effective.
- Surgery helps prevent the underlying cause from worsening.
Cons
- Surgery is an invasive procedure that carries risks such as infection, blood loss, and reactions from anaesthesia.
- Surgery can be expensive.
- Recovery time after surgery can be lengthy, requiring rehabilitation and physical therapy.
- There is no guarantee that surgery will completely eliminate pain or restore full functionality.
Conclusion
Lower back pain can come from various causes, and symptoms range from mild to severe. It can be acute, lasting for several days or weeks, or chronic, which is a recurring type of pain. In addition, the common causes of back pain include muscle strain, spinal deformities, and inflammatory conditions. It is also vital to get a proper diagnosis to identify the underlying cause. Knowing these factors can help determine the most suitable pain relief methods.
Individuals often take over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs and paracetamol to manage the symptoms. However, a doctor may prescribe stronger medicines for severe pain. Other treatment options include physical therapy, massage, and TENS therapy. These are natural and non-invasive approaches that minimise the need for medications. Finally, surgery can help provide long-lasting relief when conservative methods do not work. Ultimately, the most suitable pain relief will depend on what works best for the individual.




















