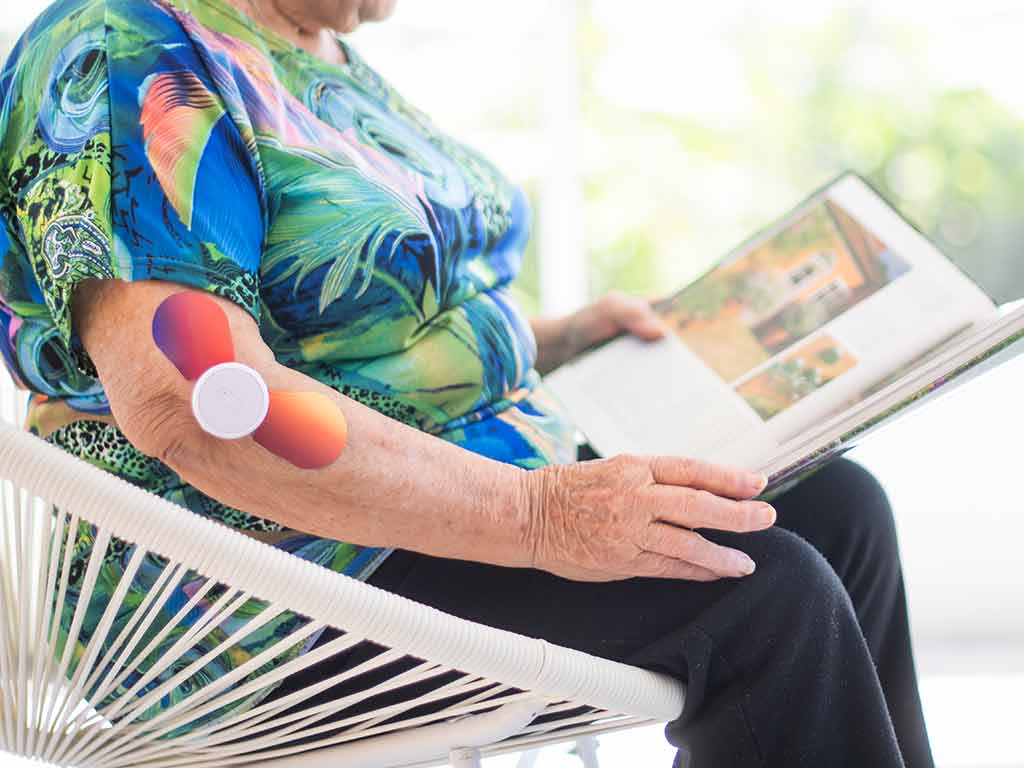

Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) are two of the most common non-invasive treatments used to relieve pain and promote muscle recovery. TENS EMS machines use electrical impulses sent to the body to stimulate the nerves and the muscles. They provide a safe and effective way to address pain conditions like arthritis, sciatica, and injuries. Each type of therapy serves a specific purpose. Thus, knowing the particular condition is vital to choosing the correct device.
Electrical stimulation is a form of therapy used in clinical settings to manage pain and improve physical conditions. Fortunately, the availability of portable devices enables individuals to manage their pain and recovery at home. The stimulation machines are easy and convenient to use anytime, anywhere. In this article, we will explore the principles of EMS and TENS therapies, how they work, and the conditions they can treat.
What are TENS and EMS Therapy?
TENS therapy is a pain management method that uses low-voltage electrical currents to the affected area of the body. These currents target the nerves to help disrupt and block pain signals, resulting in temporary relief. Pain management specialists use it to treat acute and chronic pain in patients. This drug-free pain relief is an ideal alternative for individuals who want to avoid the side effects of medications.
On the other hand, EMS therapy focuses on stimulating the muscles to contract and relax repeatedly. It uses stronger currents than TENS, which helps to strengthen and rehabilitate the muscles. It is often a part of physical therapy programs to help patients regain strength and mobility after an injury or surgery.
The electrical stimulation machines are available in separate units. People with chronic conditions may use the TENS machine in their daily routines. Meanwhile, athletes and people with sports injuries may utilise EMS devices for recovery and enhance their performance. Combined TENS EMS units are also available for comprehensive stimulation therapy.
Brief History of Electrical Stimulation
- 1st century AD: Ancient Egyptians used electric fish to treat pain.
- 18th century: Luigi Galvani experimented with electrical stimulation on muscle tissues, laying the foundation for modern electrotherapy.
- Late 19th century: The development of the first electrical stimulators for medical use, primarily for treating pain and muscle weakness.
- Early 20th century: The use of electrical stimulation for rehabilitation purposes gained popularity, especially in treating neurological disorders.
- 1950s: Introduction of TENS for pain relief. Dr. Norman Shealy is credited for the development of the modern TENS unit.
- Present: Electrical stimulation is widely applicable in various fields, including pain management, physical therapy, and sports training.
How TENS and EMS Works
TENS and EMS work on the principle of stimulating cells in the body using electrical impulses. The machines use adhesive electrodes on the skin to deliver these pulses. TENS therapy, in particular, uses varying frequencies to activate the natural pain mechanisms of the body. Firstly, low-frequency TENS currents (2-10 Hz) aim to induce the production of endorphins, the natural painkillers.
Secondly, high-frequency TENS currents (50-120 Hz) are ideal for stimulating the nerve fibres that act as “gates” to block the transmission of pain signals in the spinal cord. Consequently, the brain receives fewer pain messages, resulting in a decrease in pain perception. The gentle electrical pulses also improve blood circulation and reduce inflammation.
In comparison, EMS therapy sends higher-frequency electrical signals that directly target muscle groups, causing them to contract. This contraction is vital for muscle strengthening, neuromuscular reeducation, mobility, and enhancement of overall muscle performance. The machines have adjustable pulse width, pulse rate, and intensity to cater to different comfort levels or specific treatment needs.
Difference Between EMS and TENS
The key differences between the two types of stimulation are how they work and the outcomes they aim to achieve. Primarily, TENS target nerves for pain relief, while EMS focuses on the muscles for strengthening and rehabilitation. In addition, TENS operates on lower frequency ranges, while EMS uses stronger currents for contractions.
The electrode placement of TENS is typically around the area of pain, while EMS electrodes should be directly on multiple muscle groups. Moreover, TENS can be for passive treatment, whereas EMS complements an active workout. Lastly, individuals can use a TENS machine daily, while EMS needs an interval of a few days.
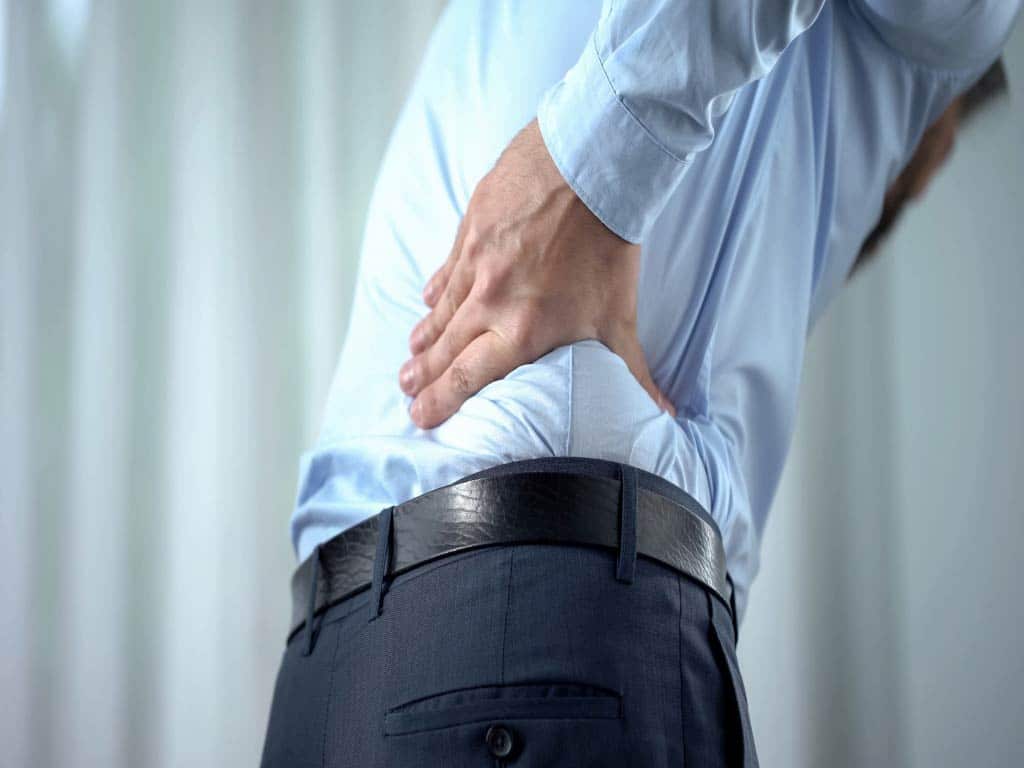

Types of Pain that Can be Treated with TENS and EMS
TENS and EMS devices are effective in managing various types of pain and conditions. TENS therapy helps alleviate acute pain like muscle strains, headaches, and labour pain. Women may also experience calmer period pain with the device by easing muscle spasms and cramping sensations. Furthermore, TENS can help relieve post-operative pain, including swelling in the surgical area.
Another main benefit of TENS therapy is the management of chronic or ongoing pain. These are conditions that have recurring pain symptoms due to underlying health issues or disorders. This includes joint pain, musculoskeletal pain, and neuropathic pain. Many TENS digital machines have preset programs for back pain, sciatica, fibromyalgia, and arthritis.
EMS devices can treat muscle pain, soreness and stiffness caused by overuse. They are commonly used in physical therapy to help individuals recover from injuries or surgery. Additionally, EMS is beneficial for people with poor blood circulation, helping them to reduce inflammation and increase their range of motion. Athletes also help to improve their muscle tone and endurance, minimising the risk of injuries.
Are There Potential Side Effects?
Side effects may occur when using these physical therapy devices. Some users may experience skin irritation or redness around the electrode site placement. This can be due to sensitivity to the adhesives of the pads or the electrical impulses. Setting the intensity to a high level when may also cause discomfort.
Overuse of the machine can also lead to muscle soreness and fatigue. Thus, it is essential to follow the usage and safety guidelines of the device to prevent any adverse effects. If side effects persist after use, consult a healthcare provider or seek medical care.
Conclusion
TENS and EMS therapy have revolutionised the field of pain management and rehabilitation. These stimulation programs offer effective and non-invasive treatment options for managing various types of pain and improving overall muscle performance. Both types of stimulation have their unique benefits and can be used in combination or separately based on individual needs. TENS blocks pain signals, providing natural pain relief, and EMS works on the muscles for strengthening and toning.
The devices have adjustable settings to cater to different pain levels and tolerance, making them suitable for a wide range of users. When used correctly and safely, EMS and TENS can help individuals improve their quality of life. While they may be convenient, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen. Electrotherapy may not be suitable for pregnant women or individuals with pacemakers, epilepsy, and heart conditions.




















