When it comes to pain management and rehabilitation, two technologies have emerged to be popular among patients and health professionals. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) are types of therapies that involve electrical impulses. However, TENS vs EMS serve different purposes. The main difference is what they target and the intended effects. TENS stimulates the nervous system to reduce pain symptoms, while EMS works on muscles for strengthening and recovery.
Many people experience pain and discomfort from various activities and conditions. Various treatments can help alleviate these symptoms, and two of the most commonly used are EMS and TENS therapies. They are non-drug and non-invasive methods that send electrical currents through the electrodes placed on the skin. However, there are a few key differences in their uses and applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the differences between EMS and TENS to determine the appropriate treatment.
Jump to a Section:
- TENS vs EMS: What Is Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation (TENS)?
- TENS vs EMS: What Can TENS Therapy Treat?
- TENS vs EMS: How Does TENS Therapy Work?
- TENS vs EMS: What Is Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS)?
- TENS vs EMS: What Can EMS Therapy Treat?
- TENS vs EMS: How Does EMS Therapy Work?
- TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are TENS and EMS Devices Safe to Use?
- TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are All TENS and EMS Units FDA Approved?
- TENS vs EMS FAQs: Which Device Should You Choose?
- TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are TENS and EMS Units the Same?
TENS vs EMS: What Is Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation (TENS)?
TENS vs EMS are similar in a lot of aspects of electrotherapy. They both apply electrical currents to the body through an external device with electrodes placed on the skin. Nevertheless, they have a few simple differences that make them distinct from each other. TENS stimulates the nerves, while EMS elicits muscle contractions.
Health professionals recommend TENS therapy to patients suffering from acute or chronic pain. They examine individual conditions to determine the appropriate settings and pad placement. Therefore, it can offer immediate pain relief through the right amount of stimulation of the nerve endings. Conveniently, individuals can manage their pain at home through portable TENS machines.
A TENS machine is a battery-operated device with a handheld control unit and adhesive electrode pads. Standard types have thin wires connecting the unit to the pads. On the other hand, wireless devices have Bluetooth capability. The stimulation can be controlled through the smartphone app, removing the inconvenience of tangled wires. Overall, it can be a drug-free pain management alternative for people who want to reduce their medicine intake.
Benefits of TENS Therapy
- TENS therapy offers non-invasive and drug-free pain relief.
- TENS can relieve various types of pain, including acute muscle soreness, chronic conditions, and even labour pain.
- It can help improve blood circulation and decrease inflammation in the body.
- TENS is a customisable treatment option that can be tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- It is safe for individuals or home use without the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- TENS therapy is an adjunctive treatment. Combining TENS with other methods can help maximise pain management benefits.
- TENS machines are practical options for people with chronic pain, as they can use them anytime they need.
TENS vs EMS: What Can TENS Therapy Treat?
TENS is a versatile and comprehensive therapy. It can treat a wide range of acute and chronic pain. Firstly, acute pain is sudden and sharp pain, often because of an injury, trauma, surgery, or illness. It usually lasts for a short time, usually less than six months, and disappears when the underlying cause has healed.
Common examples of acute pain are muscle tension and soreness due to exercise or strenuous physical activity. Another is menstrual pain, which can cause cramps. TENS is also valuable in managing labour pain and postoperative pain. Additionally, it can be effective in treating tension headaches and migraines. Many people also use a TENS machine as an electrical pulse massager.
Secondly, TENS can also effectively manage chronic pain. It is a condition that persists for an extended period, usually beyond six months, and may not have an identifiable cause. Conditions that can benefit from TENS therapy include arthritic pains, musculoskeletal pain, and nerve pains or neuropathy. Nevertheless, it is better to consult a doctor first for proper assessment to determine using TENS vs EMS for a particular condition.
What Is a TENS Machine Used For?
A TENS machine is a modality for pain management. It is commonly used in physical therapy centres or pain clinics. The electrode pads are applicable to multiple locations in the body, including the back, legs, neck, shoulder, elbow, knees, and feet. This flexibility can help relieve arthritic pain and nerve disorders.
Moreover, it is suitable for home use. Individuals can use it as often as necessary. It reduces the need for frequent doctor visits or therapy sessions. Individuals can also use the portable device at work or on the go. However, TENS may not be recommended for people with heart illness, epilepsy, and pacemakers.

TENS vs EMS: How Does TENS Therapy Work?
An essential consideration in using TENS vs EMS is how they work. Knowing their distinctions is important to use them effectively. TENS therapy utilises low-voltage electrical current to stimulate the sensory nerves and block pain signals. The treatment starts by placing the electrode pads on the skin near the pain area. Then, it delivers electric currents, causing a tingling sensation.
The electrical stimulation helps distract the brain from feeling pain. This can provide temporary relief and relaxation benefits. Furthermore, the device can also trigger endorphin release. These chemicals are known as natural pain relievers and mood enhancers. Additionally, it is vital to find the appropriate settings for optimal results.
Users can adjust the pulse rates, duration, and intensity according to their comfort level and pain tolerance. Physical therapists and healthcare providers advise starting from the lowest intensity and gradually increasing until the sensations are strong but comfortable. TENS therapy should not cause further discomfort. Following the proper usage guidelines is key for a safe and effective treatment.
The Mechanisms of Action At Work
The mechanisms of action of TENS therapy are based on two main principles. The first is the Pain Gate Control Theory. It suggests that mild electric currents can override certain nerve fibres in the spinal cord. These nerves act as “gates” that can restrict the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
The second principle is the Endogenous Opioid Release Theory. TENS therapy can trigger the production of endorphins. They are chemicals that bind to opioid receptors and inhibit them from sending pain messages to the brain. This process may take longer before a person can feel the therapeutic effects.

TENS vs EMS: What Is Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS)?
EMS is a therapy that focuses on stimulating common muscle groups rather than nerves. In comparing TENS vs EMS, an EMS machine uses stronger electrical impulses to cause muscle contractions. EMS is for therapeutic muscle stimulation and growth. It is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts to help improve muscle strength and overall muscle functions.
The main purpose of EMS therapy is to strengthen muscles, increase endurance, and improve muscle tone. It can also aid in muscle recovery after intense workouts or injuries. EMS devices have electrode pads that are placed directly on the skin over the targeted muscle groups. The session usually lasts for 15-20 minutes for several times a week.
The frequency of EMS therapy is less frequent than TENS since it uses stronger frequencies and intensities. It allows the body to recover and adapt to the muscle contractions. It is also not recommended for individuals with metal implants or pregnant women. Careful use of the device is essential to prevent any potential risks.
Benefits of EMS Therapy
- EMS therapy aims to increase muscle strength and tone. This is especially beneficial for muscles that may have been weakened due to injury or lack of use.
- It can improve blood circulation. EMS helps increase blood flow and lymphatic drainage.
- EMS therapy helps slow down or reverse muscle atrophy. This condition is the loss of muscle mass or tissue.
- EMS can help increase the range of motion for tense muscles or tendons.
- It can target specific muscle groups for focused training.
- It offers a low-impact training option for individuals with joint pain or injuries.
- EMS can enhance muscle activation and recruitment.
TENS vs EMS: What Can EMS Therapy Treat?
EMS therapy can treat a variety of conditions and injuries. One common use of an EMS machine is for muscle rehabilitation. It allows individuals to alleviate pain or discomfort from muscle damage. It includes muscle strains, sprains, and soft tissue injuries. Moreover, it can ease muscle soreness and reduce inflammation in the area.
Muscle stimulation can also be helpful for muscle-related conditions like dysphagia (trouble swallowing), fibromyalgia, stroke, and surgery recovery. It aims to increase mobility for those with limited movements. It can also help reduce the recovery time of injuries. Additionally, it relieves muscle spasms, cramps, and painful muscle knots.
The treatment applies to clinical settings, including outpatient clinics and rehabilitation centres. Patients need to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate use of the EMS device. In some cases, combining EMS with physical therapy can lead to better outcomes and faster recovery. Knowing these benefits can help individuals determine the appropriate treatment between TENS vs EMS.
What Is an EMS Machine Used For?
An EMS machine is beneficial for muscle strengthening and rehabilitation purposes. Its primary use is for injury rehabilitation. By improving blood circulation, it can help relieve pain and aid in the faster healing of injuries. It can be favourable for people with muscle weakness, paralysis, or underlying conditions.
In addition, it is useful in fitness training programs and athlete recovery tools. The therapy complements active workouts and enhances muscle endurance and tone. It can lead to better sports performance and injury prevention. Lastly, it helps minimise muscle soreness after intense workouts and plays. It has dual benefits for both rehabilitation and fitness purposes.
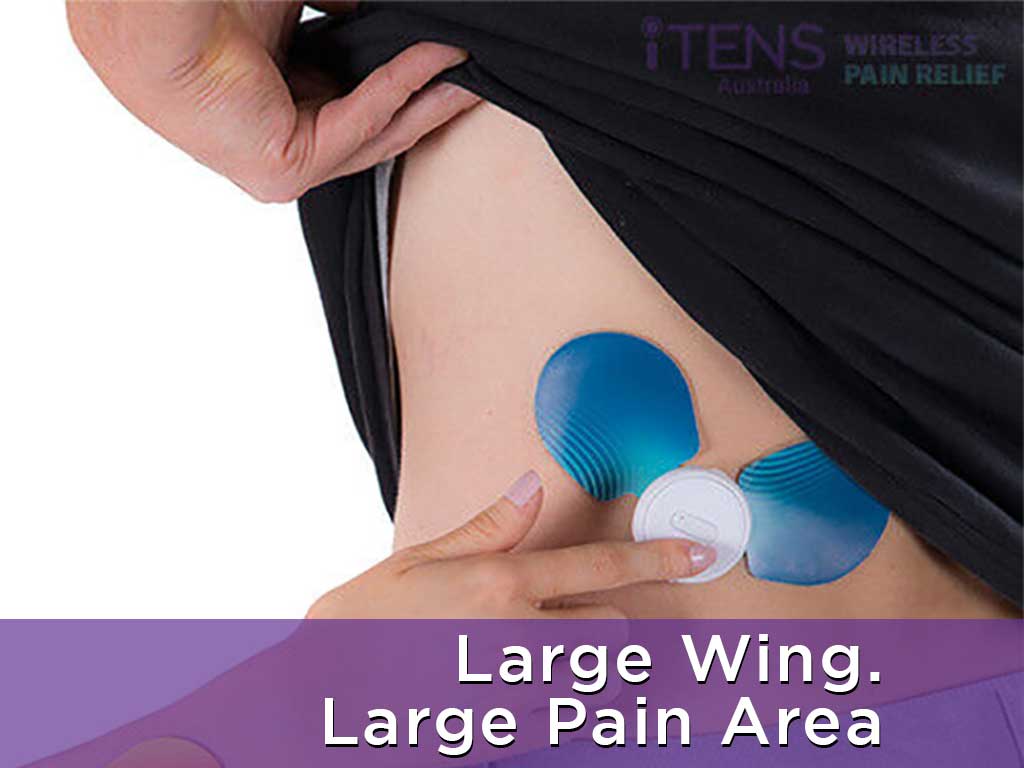
TENS vs EMS: How Does EMS Therapy Work?
EMS therapy utilises rapid electrical pulses to the muscles to contract and relax them repeatedly. This action mimics natural muscle movements during an exercise. The contraction helps strengthen and tone the muscles over time without putting strain on the joints or bones. It can also address muscle imbalances or weaknesses.
A vital consideration between TENS vs EMS is their settings. Generally, TENS machines operate on a lower frequency range. Conversely, EMS uses higher frequency and intensity levels to induce involuntary muscle contractions. Increasing the pulse width may activate more motor neurons, leading to better muscle contractions. Users may experience visible muscle twitches as a result.
Balancing the intensity and pulse duration is essential to optimise muscle contractions and comfort. A physical therapist can adjust the parameters carefully to ensure safe and effective treatment. They may try different levels to see its effects on the muscles. Individuals should also monitor how they respond to the therapy and communicate any concerns. It is important to remember that EMS machines should not be solely relied upon for muscle strengthening and re-education.
The Mechanism of Action At Work
The main mechanism of action of EMS is to mimic the signals that the brain sends to the muscles during physical activity. The electrical impulses can elicit this response from the central nervous system, causing the muscles to contract and relax. Furthermore, this contraction dilates the blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the areas that lack nutrients and oxygen.
The process also helps flush out waste products like lactic acid, reducing muscle soreness. Additionally, it triggers endorphin release, which helps in reducing muscle discomfort. By stimulating the muscles through EMS therapy, individuals can promote muscle strength, endurance, and recovery.
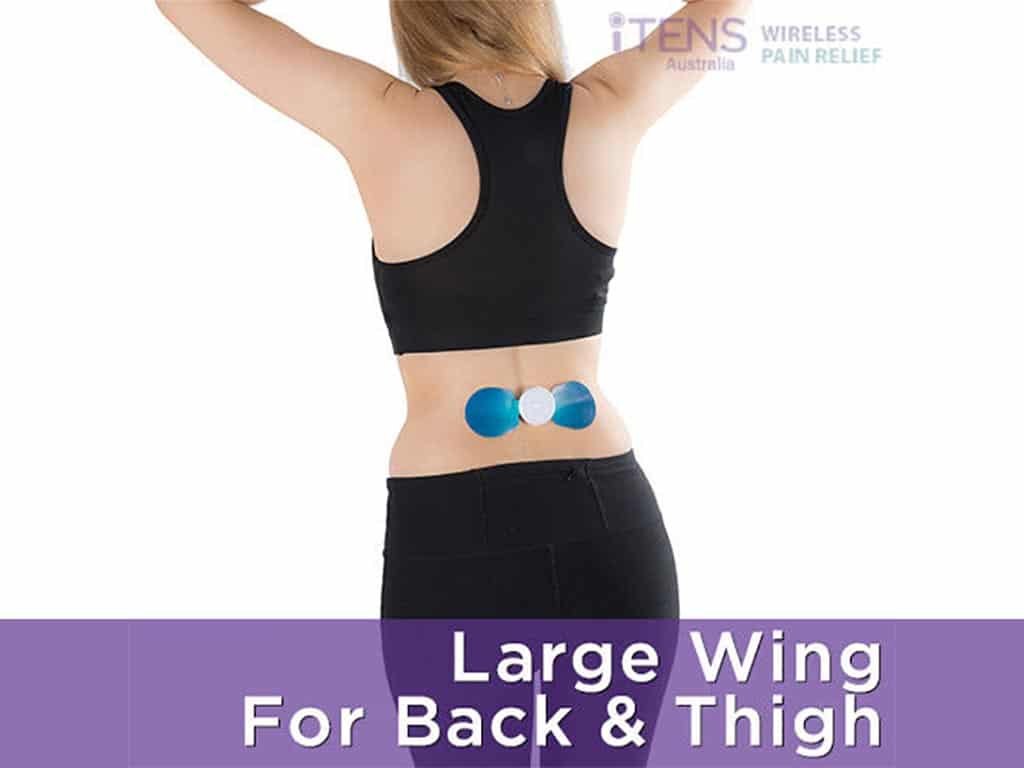
TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are TENS and EMS Devices Safe to Use?
Individuals may wonder about the safety of TENS vs EMS. Both devices are safe to use with proper usage and precautions. However, there are some important considerations to keep in mind when using these machines. While most people can safely use EMS and TENS machines, there are some exceptions. Pregnant women and individuals with pacemakers, cognitive impairment, and heart conditions should avoid using these devices.
It is also important to follow specific instructions and guidelines. It includes the treatment duration and settings. Starting at the lowest stimulation levels allows individuals to get accustomed to the electrical currents without overwhelming the body. Users may also feel a slight tingling sensation at the electrode site placement. Moreover, keep the session between 15-30 minutes at a time.
Another essential consideration is the electrode placement guide. Avoid putting the electrode pads near the eyes, heart, or broken skin. Prolonged use may cause skin irritation and muscle fatigue. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new therapy, especially if underlying health conditions are present.
Basic Safety Guidelines
- Identify the correct area of electrode placement for safe and effective use.
- Ensure the skin is clean and dry before applying the pads.
- Start at the lowest intensity and gradually increase to a comfortable level or as tolerated.
- Do not use TENS or EMS machines near sensitive areas.
- Do not use electrotherapy devices while driving, operating heavy machinery, or in water to prevent accidents.
- Avoid placing the electrodes on broken or irritated skin, as this may cause further damage or infection.
- Do not use the device while sleeping, as this may risk the electrodes coming off and causing skin burns.
TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are All TENS and EMS Units FDA Approved?
TENS and EMS are under the regulation of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA categorises TENS and EMS machines as Class II medical devices, which means they require FDA approval or clearance before being sold in the market. FDA approval indicates that the device has undergone rigorous testing to ensure its safety for consumer use.
Unfortunately, there are many devices that do not meet FDA standards and may not be approved for use. Thus, it is vital to be cautious when purchasing a TENS or EMS unit, as using a non-FDA-approved device could pose potential risks to health and well-being. Also, note that FDA approval or clearance does not necessarily guarantee the effectiveness of the treatment.
Before purchasing a device, it is essential to conduct a thorough research. Consulting with a healthcare professional can also help determine the most suitable unit between TENS vs EMS. It is best to choose a device with FDA approval or clearance to have peace of mind knowing that the unit meets the safety regulations and criteria.
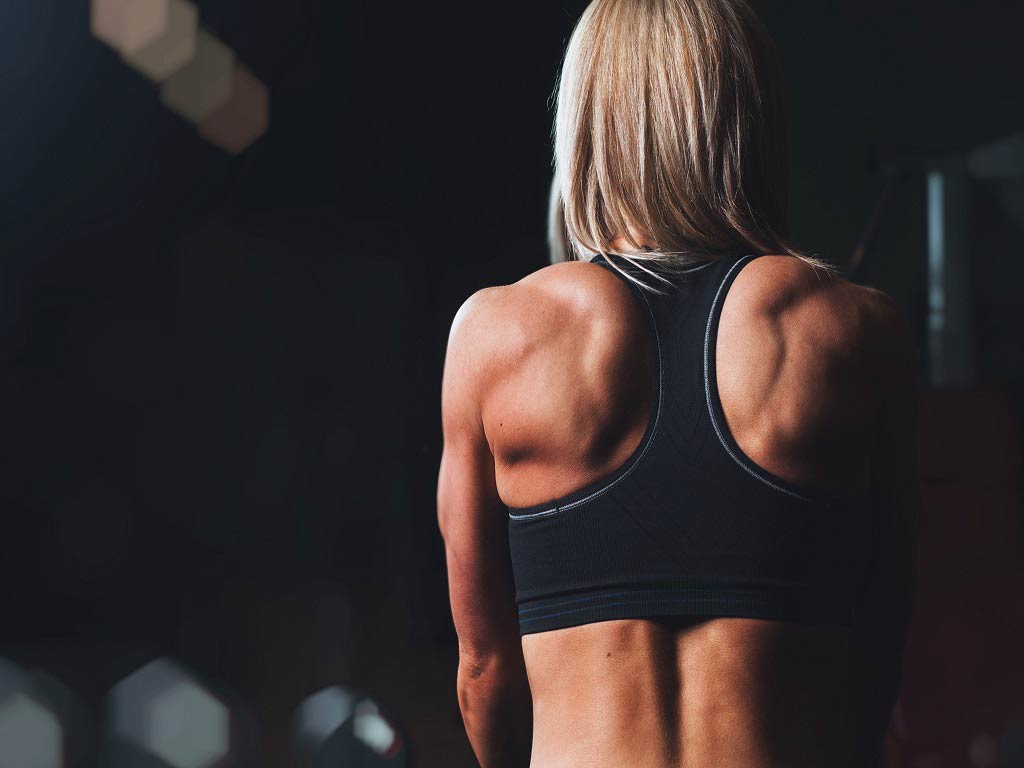
A Look at the FDA-Approved iTENS Wireless TENS Machine
The iTENS is the first wireless TENS machine with FDA clearance. This certification means that users can have confidence in using the device without professional supervision. Moreover, iTENS integrates digital technology with the effectiveness of TENS therapy. It is a wearable electrotherapy machine with enhanced portability and discreet to use.
iTENS wireless unit is Bluetooth-capable, making it controllable by a companion app on an Android or iOS device. It has a rechargeable battery and can last up to 24 hours of continuous use. Furthermore, iTENS is available in Small Wings for smaller areas and Large Wings for wider treatment coverage.

TENS vs EMS FAQs: Which Device Should You Choose?
A common challenge of TENS vs EMS is determining which device to choose. Remembering their purpose and benefits as stated above. For general pain management, a TENS machine may be more suitable as it targets chronic nerve pain and provides relief without muscle contractions. It uses milder electrical pulses, which are gentle on the skin and without the risk of adverse side effects.
On the other hand, people with muscle weakness or atrophy may benefit more from an EMS machine, as it helps strengthen and tone muscles through contractions. However, EMS machines may not be suitable for those with nerve-related pain conditions. Athletes also choose EMS machines to help with their training.
The choice between TENS and EMS devices ultimately depends on individual needs and goals. It is also worth considering if combining the two therapies can benefit the individual. Some units combine TENS and EMS functionalities. This can offer comprehensive relief, especially for people with both muscle pain and nerve-related conditions.
How to Choose the Right Option for Your Needs
When deciding which electrotherapy device to use, consider the specific needs or type of pain. Additionally, ensure that the device is safe to use. Check whether it has FDA approval or clearance. Reading the reviews and features can also help get a good quality product.
Budget is an important factor to consider when choosing a device. These products often require a significant investment. The cost of TENS and EMS machines can depend on the features and technologies they offer. It is essential to weigh the benefits of the device against its price to ensure that it meets treatment needs and provides value for money.

TENS vs EMS FAQs: Are TENS and EMS Units the Same?
TENS and EMS units may look similar on the outside, but they are different devices. They serve different purposes and have distinct functionalities. Physically, they have the same components, such as electrodes and a control unit. The control unit consists of dials or buttons to control the intensity, frequency, and pulse duration. It also has an LCD screen display for viewing the current settings and monitoring the treatment.
The difference between TENS vs EMS is in their range of settings. EMS produces higher frequency levels targeting muscle stimulation. The currents from EMS can reach deep muscle fibres, while TENS focuses on superficial nerves. In addition, EMS machines present different modes for muscle pain and massage.
On the other hand, many TENS machines have pre-set programs for various pain conditions like arthritis, sciatica, fibromyalgia, and tendonitis. Nevertheless, some TENS devices may include EMS functions, such as massage and muscle relaxation. It is important to check the parameters of each device to see if they can be used for other purposes.
Summary of the Differences
- TENS therapy is for pain management, while EMS is for muscle strengthening and neuromuscular re-education.
- TENS targets nerves, while EMS work on key muscle groups.
- A TENS machine uses a lower frequency, while an EMS device operates on a higher frequency range.
- TENS is more suitable to treat chronic pain conditions.
- EMS is effective for acute muscle pain and rehabilitation after injuries.
- The electrode placement for TENS is near the affected nerves. The pad placement for EMS is over the targeted muscle groups.
- A TENS machine can be used multiple times daily. EMS treatments are limited to one 20-minute session.
Conclusion
TENS and EMS are two common electrotherapies that individuals use in various situations. They both use a portable device to deliver electrical currents to the body. However, TENS vs EMS have different purposes. TENS therapy stimulates the nerves for pain relief. It can treat a wide range of ailments, including joint pain, neuropathy, and muscular pain. It works by blocking pain signals and releasing endorphins, reducing the severity of pain symptoms.
Meanwhile, EMS works on the muscles to induce contractions. This can help increase strength and restore mobility. It also helps boost blood circulation, which promotes the faster healing of injured muscles and tissues. Furthermore, understanding the differences in their functionalities and benefits can help determine which device is more suitable for a specific condition or treatment goal. It is advisable to consult a health professional before starting any therapy to determine the correct settings and other instructions.