
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a therapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to stimulate the sensory nerves. It does this using TENS machines to deliver electrical stimulation to the body. The devices have adjustable settings that allow people to control the electronic stimulation. TENS sensory stimulation alleviates aches for acute and chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia and sciatica, by triggering the pain gate mechanism and the release of endorphins.
TENS therapy is commonly used in medical settings due to its beneficial effects. It works well as an adjunct therapy for other treatments and increases the speed of rehabilitation. People can also use electric therapy stimulators in their homes by buying a personal unit. They are easy to use even without medical supervision. These are available in online and physical stores. This article will present information on TENS, its mechanisms of action, and its applications.
Overview of TENS Sensory Stimulation
TENS sensory stimulation is a therapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief. In clinical practice, many healthcare professionals use these electrical stimulation devices to alleviate pain within a short time. People can also use a TENS machine in their homes by purchasing or renting a personal unit.
Stroke patients and diabetic patients are some of the people whom healthcare providers may recommend TENS therapy. They can benefit from the relief it provides and experience better rehabilitation outcomes with this adjunct therapy. Some find that using TENS can improve results from tests of motor function. They are also safe for elderly people who experience constant body aches to use.
Generally, TENS machines comprise a control unit and electrode pads. To use the device, attach the electrode pads to the target areas. Afterwards, connect the controller and the pads using lead cables or Bluetooth. Once secure, they may turn the unit on and adjust the settings accordingly. A session typically lasts between 20 and 30 minutes.
How TENS Targets Sensory Nerves
- TENS therapy can target the sensory nerves using strategic placement of the electrode pads. Selecting appropriately sized pads also contributes to this.
- The electrical impulses travel from the power source to the electrodes, then the skin.
- Once the pulses reach the skin, they travel along the sensory nerves to activate mechanisms for relief.
- People may start feeling tingling sensations or electrical noise that helps distract against aches.
- By causing these sensations, TENS can disrupt pain signals and reduce the perception of pain in people.
- Users can adjust the electric nerve stimulation by adjusting the settings according to their comfort level.
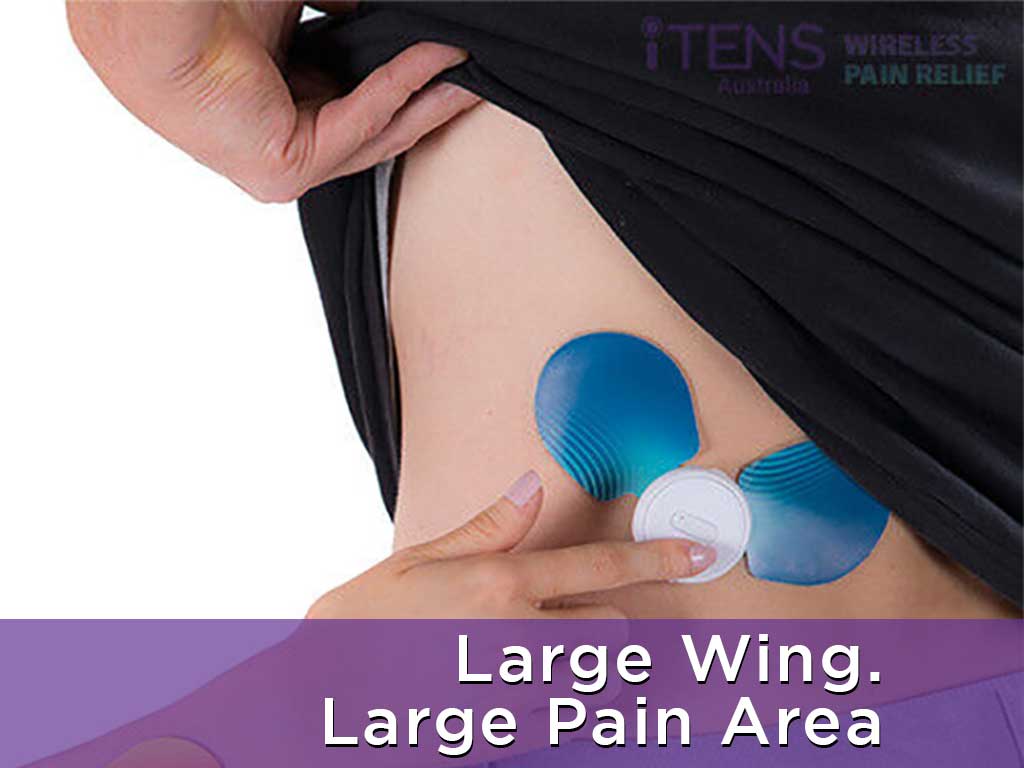
Mechanisms of Action Behind TENS Sensory Stimulation
TENS sensory stimulation involves activating mechanisms of action in the body for relief. The first of which is the pain gate mechanism. This is an idea proposed in the Gate Control Theory of Pain. It suggests that electrical pulses from TENS can stimulate the spinal nerve cells to close “gates” and block the painful signals from reaching the brain. Users can trigger this with high frequencies.
Another mechanism TENS can trigger with high-frequency stimulation is vasodilation near the target area. This improves blood flow, which helps reduce muscle soreness and can enhance the healing of injuries. It can also help reduce inflammation to help regain motor function.
Lastly, TENS is also thought to provide motor-level stimulation using low frequencies. This triggers the production of endorphins. These hormones bind to opioid receptors for lasting relief from aches. Endorphins from motor TENS stimulation also help improve moods and promote a better sense of well-being. Overall, TENS induces natural mechanisms to alleviate pain from various conditions.
Frequencies and Intensities
TENS stimulators typically have adjustable intensity and frequency levels. Frequency refers to the number of electrical pulses delivered per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). Many use higher frequencies for acute pain relief, while lower frequencies are more suitable for chronic pain management.
Meanwhile, intensity refers to the strength of the electrical impulses. It is measured in milliamperes (mA). It can be adjusted to suit individual comfort levels. When using TENS, it is generally recommended to start with low intensities since it can cause electric shocks or discomfort. It may also cause skin irritation underneath the electrode sites if the level is too high.
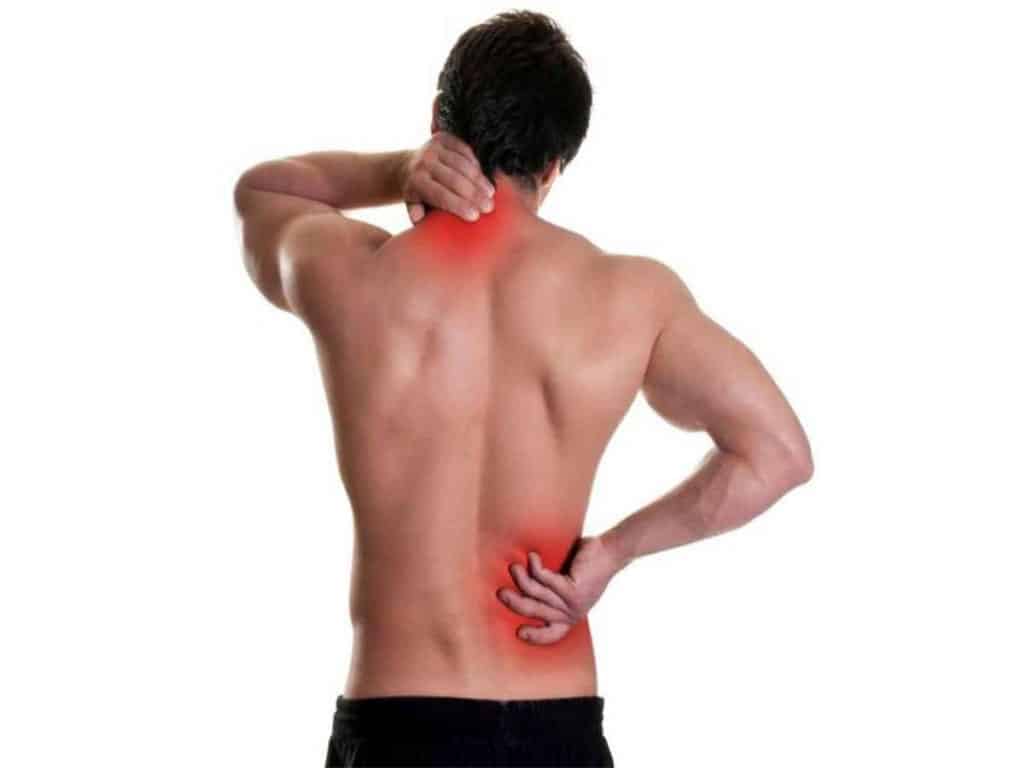
Applications of TENS Sensory Stimulation in Pain Management
TENS sensory stimulation has several applications in pain management. It has several beneficial effects that help people with various conditions. Firstly, it helps with acute pain. These are conditions that do not last more than six months. Some stem from injuries and fade during recovery or rehabilitation. Examples include postoperative pain, headaches, and primary dysmenorrhea.
TENS also helps with chronic pain conditions. These are aches that last for more than six months. They can be due to underlying medical conditions or unexplained reasons. Fibromyalgia, which causes widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in patients, is one example of this. Many forms of arthritis also fall under this as they worsen over time.
TENS therapy also shows positive responses when used for neuropathic pain. Electrical stimulation can ease aches from conditions caused by nerve damage or injuries. This includes diabetic neuropathy, venous insufficiency, sciatica, and Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Overall, TENS provides versatile relief that benefits many patients in and out of medical settings.
Benefits of TENS
The foremost benefit of TENS is the natural pain relief it provides. It is a non-invasive treatment, eliminating the chances of infections common to surgical procedures. Moreover, transcutaneous stimulation has minimal risks in comparison to oral medications. They can also help reduce the intake of these medications to decrease the risks of long-term side effects.
Besides reducing pain, TENS can also help with other treatments during rehabilitation. It is safe for neuropathic patients and those undergoing post-stroke rehabilitation. It can provide relief using convenient preset stimulation modes. With user-friendly features and preset programs, patients can easily self-administer treatment using the wide intensity and frequency range.
Conclusion
TENS sensory stimulation is an effective method of alleviating pain from various conditions. This treatment uses low-voltage electric pulses to trigger the sensory nerves to block pain signals. In addition, motor TENS stimulation induces the production of endorphins. By using electric stimulation for these effects, TENS provides drug-free and non-invasive relief to many patients. Moreover, it can contribute to improved performance on motor function tests since it can help improve blood circulation for healing.
TENS works for several conditions with minimal risks. It can address acute conditions like primary dysmenorrhea and headaches. Many chronic pain patients also experience positive outcomes from using TENS stimulators. With user-friendly features and portable designs, TENS is growing in popularity as an alternative method for relief. Nevertheless, individuals should consult a healthcare provider before using one to ensure safety. Those interested in using a TENS machine may consider the iTENS from iTENS Australia.




















