
A bulging disc in the lower back or lumbar disc bulge is a condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the spine. It occurs when the outer layer of the disc weakens or tears, causing the inner gel-like material to protrude. This condition can be caused by various factors, including degenerative disc disease, improper lifting techniques, and a sedentary lifestyle. Treatment options typically involve physical therapy, pain medication, and Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) therapy.
Living with a lumbar disc bulge can be a challenging experience. People with this condition may experience pain, numbness, or tingling in the affected area. They may also have difficulty performing everyday tasks and may need to make certain lifestyle adjustments. It is important for individuals with bulging discs to seek medical advice and follow a treatment plan. This article will present what is a lumbar disc bulge, including its causes and treatments.
What Is Bulging Disc In Lower Back
A bulging disc in the lower back is a condition where one of the intervertebral discs protrudes or bulges out. These discs act as cushions to absorb shock and provide flexibility to the spine. When a disc bulges, it may put pressure on nearby nerve roots or the spinal canal, causing pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of a lumbar disc bulge can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include leg pain, muscle weakness, and numbness or tingling in the legs or feet. Additionally, some individuals may also experience difficulty with certain movements or normal activities. In severe cases, a bulging disc can compress the sciatic nerve, leading to sharp pain and limited mobility.
If left untreated, a lumbar disc bulge can potentially worsen and lead to more serious complications. The bulge may progress into a herniated disc, where the inner disc material leaks out through the outer wall. This can result in additional symptoms such as bladder or bowel control issues. Chronic pain and the inability to carry out regular activities can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life.
How To Prevent
- Maintain regular physical activity: help strengthen the muscles in the lower back and abdomen, providing support to the spine.
- Practice proper lifting techniques: avoid lifting objects using improper techniques, as this can put strain on the lower back.
- Maintain a healthy weight: excess weight can place extra stress on the spine, leading to disc degeneration and bulging.
- Avoid prolonged sitting: sitting for long periods can increase pressure on the lumbar spine.
- Practice good posture: maintaining proper posture throughout the day can help reduce strain on the lower back.
- Avoid repetitive movements: repeating the same motion or activity continuously can increase the risk of disc damage.
Common Causes Of Bulging Disc In Lower Back
There are several common causes of a bulging disc in the lower back. Firstly, degenerative disc disease, which is the natural wear and tear of the spinal discs over time. As individuals grow older, the discs may gradually lose water content and become less flexible. This makes them more prone to bulging or herniation.
Secondly, improper lifting techniques or heavy lifting can also lead to a lumbar disc bulge. When a person lifts a heavy object using their lower back, excessive pressure can be placed on the spinal discs. This can cause the outer layer of the disc to bulge outwards, resulting in a bulging disc.
Lastly, a sedentary lifestyle with limited physical activity can contribute to the development of a lumbar disc bulge. Lack of regular exercise and prolonged sitting can weaken the muscles that support the spine. This leads to imbalances and increased stress on the spinal discs. Over time, this can cause the disc to bulge. Therefore, people should ensure they have an active lifestyle and practice proper lifting techniques.
Risk Factors
A bulging disc can be caused by various risk factors. Excess body weight puts added strain on the spinal column. Physically demanding jobs that involve repetitive lifting or bending also contribute to the condition. Improper lifting techniques can put excessive pressure on the spinal discs, leading to protrusions.
Additionally, genetics can also play a role in the development of a lumbar disc bulge. Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to have weaker outer layers of their intervertebral discs, making them more susceptible. Moreover, a sedentary lifestyle can weaken the muscles that support the spinal column, making it easier for discs to bulge.
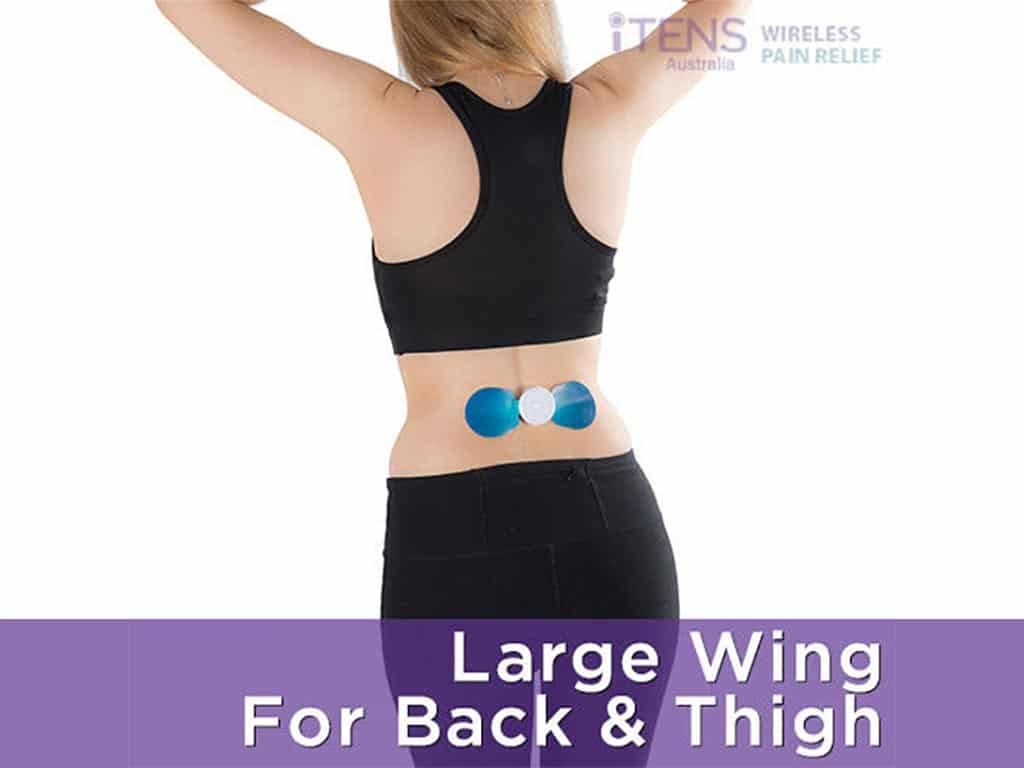
Treatments For Bulging Disc In Lower Back
A bulging disc in the lower back can impact daily activities and quality of life. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available that can help alleviate symptoms and improve function. Physical therapy is often recommended as a first-line treatment for a lumbar disc bulge. This involves exercises and stretches that target the muscles supporting the spine, enhance flexibility, and reduce pressure.
In addition to physical therapy, pain medication can also play a role in managing the pain associated with a lumbar disc bulge. Doctors may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relievers to reduce inflammation and ease the pain. Additionally, muscle relaxants can also be prescribed to relieve muscle spasms that may occur.
Moreover, individuals may consider TENS therapy as a potential treatment for pain relief. This therapy utilises a compact device, such as iTENS, which administers low-voltage electrical impulses to the specific pain area. These impulses actively work to stop the transmission of pain signals to the brain, offering a brief respite from any discomfort.
Diagnosis And Nerve Tests
When doctors diagnose a lumbar disc bulge, they usually begin by performing a comprehensive physical examination. They may ask about the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and any recent injuries. To confirm the diagnosis, they may suggest imaging tests like an MRI scan. These tests can provide detailed images of the spine.
Additionally, healthcare providers can conduct various nerve tests to assess the functionality of nerves. One such test is the Nerve Conduction Study (NCS), which assesses how well electrical signals travel through the nerves. Another test is the electromyogram (EMG), which involves inserting tiny needles into the muscles to identify muscle weakness.
Conclusion
A bulging disc in the lower back happens when one of the discs between the vertebrae protrudes or bulges out. This can occur due to degenerative disc disease, improper lifting methods, or a sedentary lifestyle. Fortunately, there are effective treatments available to ease symptoms and enhance functionality. Physical therapy, pain medication, and TENS therapy are commonly utilised to manage the pain linked to a lumbar disc bulge.
To prevent and treat the condition, individuals need to understand the factors that increase the risk. These include being overweight, having physically demanding jobs, lifting objects incorrectly, having a genetic predisposition, and leading a sedentary lifestyle. Physical examinations and imaging tests, such as an MRI scan, can provide a thorough diagnosis. Nerve tests such as the NCS and EMG can also assess nerve functionality. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can maintain a healthy spine.







