In recent years, TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) machines have gained popularity for relieving pain and improving muscle function. These portable devices have become accessible for home use, providing individuals with a non-invasive and drug-free method to manage their condition. TENS and EMS machines work using electrical currents to block pain signals and reduce inflammation. Thus, it provides many benefits, such as temporary relief and faster rehabilitation from injuries.
Acute or chronic pain affects many people daily. This can limit their activities and cause stress. Underlying health conditions are common factors. In addition, discomfort can come from work or physical activities that result in sore and tight muscles. Hence, therapies like TENS and EMS are helpful for individuals dealing with various conditions. This article will delve into the key essentials of TENS and EMS units, how they work, and the benefits of using them.
What are TENS and EMS Machines?
TENS and EMS machines are battery-operated devices that use electrodes to deliver electrical impulses to address pain and mobility issues. Both machines have a small pulse generator, adjustable controls, and adhesive pads. Additionally, standard devices use lead wires, while some have wireless electrodes, like the iTENS. However, they serve distinct purposes.
TENS machines are primarily designed for pain management. It utilises low-voltage electrical currents to stimulate the sensory nerve endings to reduce pain. The currents are adequate for activating the pain relief mechanisms of the central nervous system but mild enough not to harm the nearby tissues. Contemporary TENS units have dual operations, including customisable settings and preset programs.
On the one hand, EMS machines focus on muscle strengthening and rehabilitation. It uses stronger electrical pulses to induce muscle contractions. Fitness trainers include EMS therapy in their sports or training programs to enhance overall muscle performance. Likewise, physical therapists use EMS machines for post-injury rehabilitation. Devices with advanced technology include massage stimulation programs and therapeutic muscle stimulation modes.
Brief History of TENS and EMS
- Electrical stimulation dates back to 63 AD when Scribonius Largus recorded that patients could relieve pain by standing near electrical fish.
- Electrostatic devices were invented throughout the 16th to 18th centuries to treat headaches and other pains.
- In the 18th century, Luigi Galvani discovered electric muscle stimulation by providing scientific evidence that currents can induce muscle movement.
- In the 1970s, the first modern, patient-wearable TENS machine became available. TENS therapy gained recognition as a non-invasive pain relief method.
- Portable devices were further developed in the 21st century, making electrotherapy more accessible for individuals suffering from chronic back pain, arthritis, and other nerve-related conditions.
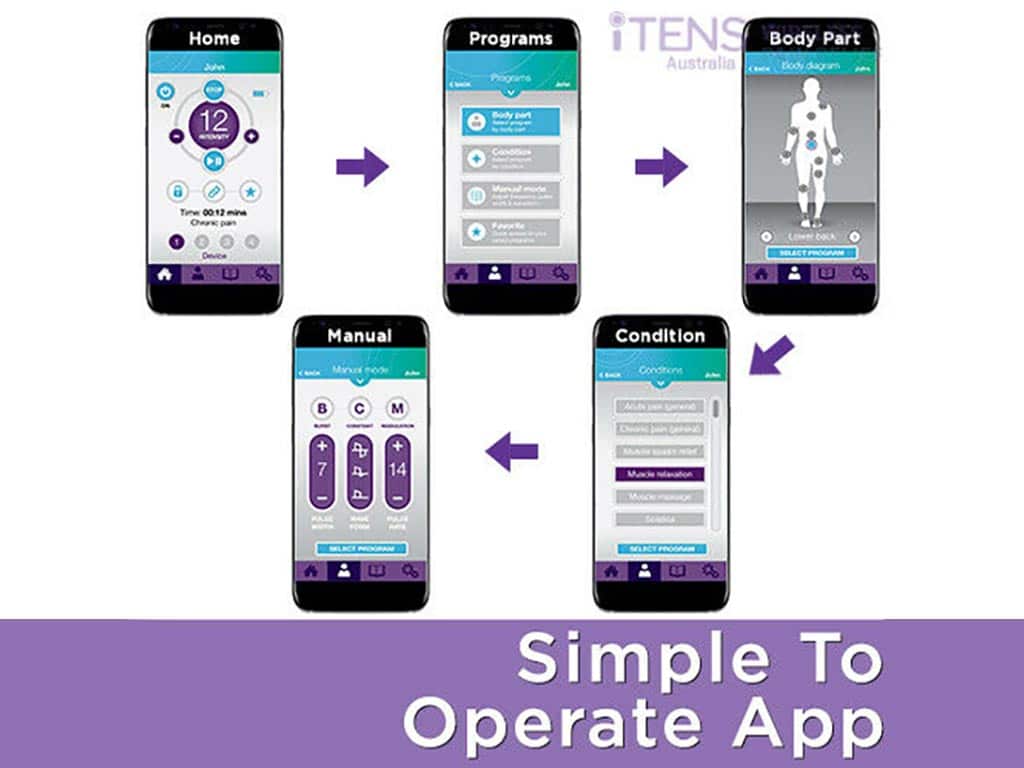
How TENS and EMS Machines Work
Both TENS and EMS machines work by applying electrical currents to the body, but they target different areas and serve different purposes. TENS machines override the central nervous system, particularly the pain gate mechanism. It causes the nerve fibres in the spinal cord to close, blocking the pain signals travelling to the brain. Additionally, it stimulates the release of endorphins, the natural painkillers.
EMS machines send stronger doses of electrical impulses from electrodes to stimulate the motor nerves. These nerves are responsible for eliciting muscle vibrations. The impulses send signals to the brain to mimic natural contractions of the muscles. As a result, the contractions help to strengthen and tone the muscles.
The stimulation from TENS and EMS are also effective in boosting blood circulation. It dilates the blood vessels, distributing more oxygen and nutrients to the affected area. The increase in blood flow helps reduce swelling and release muscle tension. By relaxing the muscles, it helps to restore the range of motion.
Understanding Frequencies and Intensities
The frequency refers to the number of pulses per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). Low-frequency TENS currents (1-10 Hz) facilitate endorphin production. In contrast, high-frequency TENS currents (50-130 Hz) produce a strong but comfortable sensation to block pain signals. Meanwhile, EMS use 50 Hz and above to target fast-twitch muscle fibres.
The intensity or amplitude refers to the strength of the electrical current. Individuals can set the intensity to a maximum tolerable range to induce muscle contractions for EMS training. They are adjustable to suit individual preferences and needs. However, users should start with the lowest intensity levels to prevent sudden shocks or discomfort.
Benefits of TENS and EMS Machines
TENS and EMS machines offer numerous benefits for individuals seeking pain relief or muscle stimulation. One of the main benefits of these devices is its non-invasive approach. They have adhesive electrodes for external application. They are comfortable and painless to use, as they do not penetrate the skin or leave permanent marks.
Another significant benefit and advantage is their drug-free nature. TENS and EMS do not use medications, which avoids systemic side effects or risk of dependence. Moreover, they offer fast and temporary pain relief. They can treat a wide range of conditions, ranging from acute muscle soreness to chronic nerve pain. Some devices, like iTENS, combine TENS and EMS benefits.
Furthermore, regular use of the device can show significant improvements in muscle tone, strength, endurance, and overall performance. It can help individuals recover from injuries faster and improve their athletic abilities. Lastly, they are versatile devices. The machines offer a range of programs to cater to individual needs. This makes them cost-effective in physical therapy or pain management programs, as they can address multiple issues from one device.
Treatable Conditions
TENS and EMS can manage a wide range of issues. TENS therapy provides symptomatic relief for acute and chronic pain. It includes conditions such as fibromyalgia, joint pains, and neuropathic pains. In addition, it can provide effective relief for headaches, period pain, labour pain, and postoperative pain.
EMS, on the other hand, is effective for relieving muscle spasms, cramps, and muscle pain. It helps prevent and minimise discomfort and soreness, usually after intense workouts. Moreover, it helps prevent muscle atrophy and reverses poor blood circulation. Thus, EMS is ideal for rehabilitation from injury, post-surgery, paralysis, and other mobility issues.
Conclusion
TENS and EMS machines are two of the most widely used tools in modern-day physical therapy. They generate small electrical currents to stimulate the nerves or muscle groups. However, each operates on different frequency and intensity levels to attain specific outcomes, such as alleviating pain and rehabilitating the muscles. This approach is non-invasive and drug-free. In addition, these devices are portable and easy to use. Individuals can use them at home whenever they need without going to a treatment centre.
Knowing the difference between TENS and EMS can help determine the correct device to use. TENS targets the nerves to help block pain signals and release endorphins. Conversely, EMS works on key muscles to stimulate contractions. Both devices have adjustable settings and preset programs to manage a wide array of conditions. Nevertheless, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to ensure proper usage and treatment plan.